
浙江农业科学 ›› 2026, Vol. 67 ›› Issue (1): 231-242.DOI: 10.16178/j.issn.0528-9017.20240775
倪金洋1,2( ), 王峰2, 俞巧钢2, 周俊3, 孙万春2, 马式太1,2, 吕勇杰4, 马军伟1,2,*(
), 王峰2, 俞巧钢2, 周俊3, 孙万春2, 马式太1,2, 吕勇杰4, 马军伟1,2,*( )
)
收稿日期:2024-09-29
出版日期:2026-01-11
发布日期:2026-01-19
通讯作者:
马军伟
作者简介:马军伟,E-mail:majw111@126.com。基金资助:
NI Jinyang1,2( ), WANG Feng2, YU Qiaogang2, ZHOU Jun3, SUN Wanchun2, MA Shitai1,2, LYU Yongjie4, MA Junwei1,2,*(
), WANG Feng2, YU Qiaogang2, ZHOU Jun3, SUN Wanchun2, MA Shitai1,2, LYU Yongjie4, MA Junwei1,2,*( )
)
Received:2024-09-29
Online:2026-01-11
Published:2026-01-19
Contact:
MA Junwei
摘要:
自20世纪50年代以来,我国南方酸性土壤面积明显增加,对土壤肥力、作物生长发育及产量品质、粮食安全、农业经济和生态环境造成的不利影响日益严重。南方一带雨水量大且集中,由此引发的土地侵蚀与养分流失严重,导致土壤碱性成分钙、镁、钾等元素大量淋失。南方一带工业生产所造成的酸雨与农业活动中不恰当的耕种手段等多重因素叠加,加剧了南方耕地土壤酸化。本文从时代发展角度和区域差异角度详细描述了我国南方在不同历史时期土壤酸化发生的特点及其关键影响因素,概述了针对土壤酸化的阻控技术和相关领域研究进展,并对未来土壤酸化领域的研究趋势进行了预测,旨在为深入探究土壤酸化的形成机制、优化预测模型,进而推广有效的土壤酸化治理方法,有效遏制并扭转土壤酸化态势提供支持。
中图分类号:
倪金洋, 王峰, 俞巧钢, 周俊, 孙万春, 马式太, 吕勇杰, 马军伟. 1950—2020年我国南方土壤酸化的演变特征及治理技术研究进展[J]. 浙江农业科学, 2026, 67(1): 231-242.
NI Jinyang, WANG Feng, YU Qiaogang, ZHOU Jun, SUN Wanchun, MA Shitai, LYU Yongjie, MA Junwei. Evolution characteristics and improvement technology research progress of soil acidification in southern China from 1950 to 2020[J]. Journal of Zhejiang Agricultural Sciences, 2026, 67(1): 231-242.
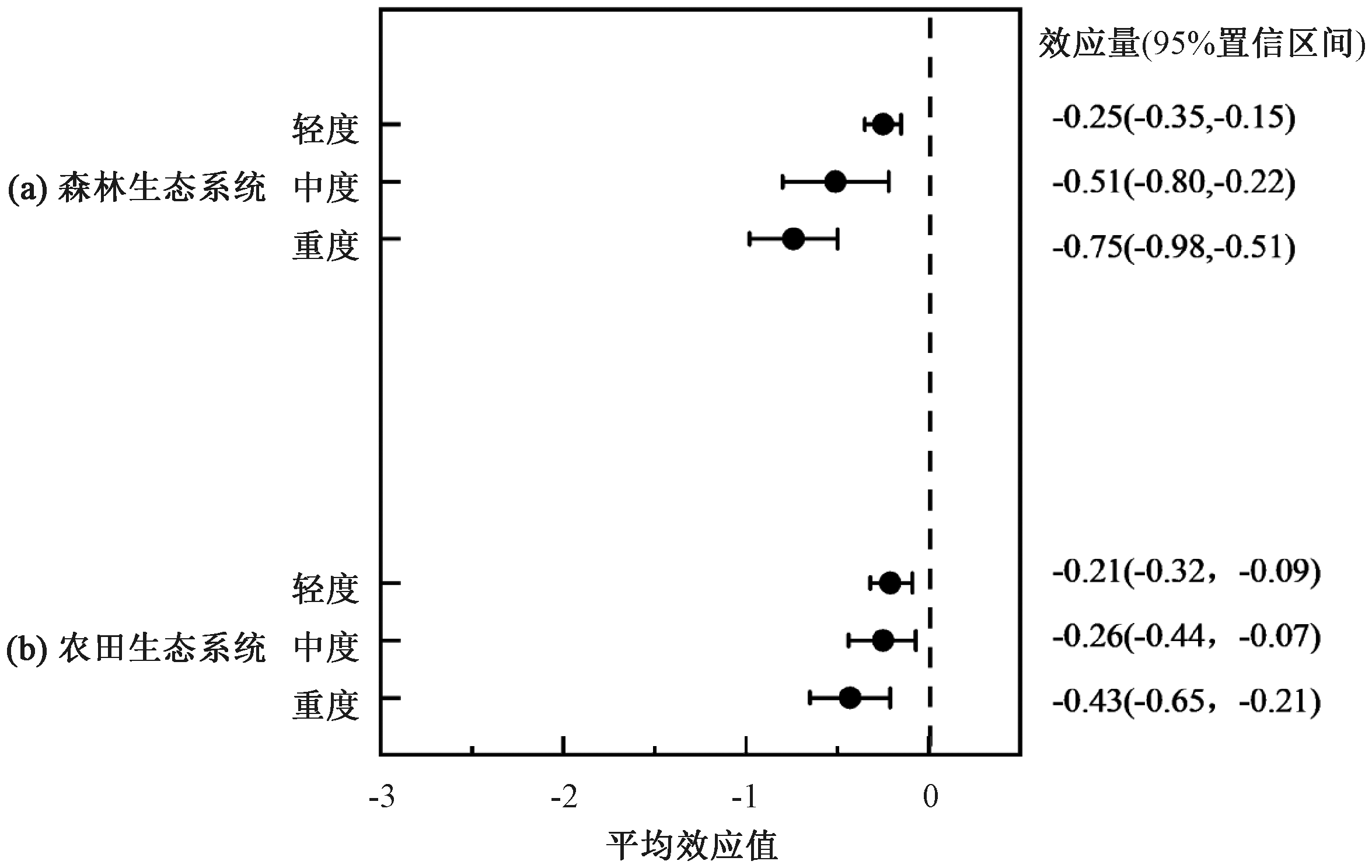
图1 模拟酸雨对农田和森林生态系统土壤pH值的影响 括号内数值代表效应区间。若效应区间不与0重叠,则表明显著(p<0.05)增加(>0)或显著减少(<0)。横坐标表示pH值下降数值。图2同。
Fig.1 Effect of simulated acid rain on the pH value of soil in farmland and forest ecosystems
| [1] | REGELINK I C, STOOF C R, ROUSSEVA S, et al. Linkages between aggregate formation, porosity and soil chemical properties[J]. Geoderma, 2015, 247: 24-37. |
| [2] | HAYNES R J, SWIFT R S. Effects of soil acidification and subsequent leaching on levels of extractable nutrients in a soil[J]. Plant and Soil, 1986, 95(3): 327-336. |
| [3] | ZHU H H, CHEN C, XU C, et al. Effects of soil acidification and liming on the phytoavailability of cadmium in paddy soils of central subtropical China[J]. Environmental Pollution, 2016, 219: 99-106. |
| [4] | NAZ M, DAI Z C, HUSSAIN S, et al. The soil pH and heavy metals revealed their impact on soil microbial community[J]. Journal of Environmental Management, 2022, 321: 115770. |
| [5] | PHILIPPOT L, CHENU C, KAPPLER A, et al. The interplay between microbial communities and soil properties[J]. Nature Reviews Microbiology, 2023, 22(4): 226-239. |
| [6] | 郑超, 郭治兴, 袁宇志, 等. 广东省不同区域农田土壤酸化时空变化及其影响因素[J]. 应用生态学报, 2019, 30(2): 593-601. |
| ZHENG C, GUO Z X, YUAN Y Z, et al. Spatial and temporal changes of farmland soil acidification and their influencing factors in different regions of Guangdong Province, China[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2019, 30(2): 593-601. | |
| [7] | 张玲玉, 赵学强, 沈仁芳. 土壤酸化及其生态效应[J]. 生态学杂志, 2019, 38(6): 1900-1908. |
| ZHANG L Y, ZHAO X Q, SHEN R F. Soil acidification and its ecological effects[J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 2019, 38(6): 1900-1908. | |
| [8] | 于天仁. 中国土壤的酸度特点和酸化问题[J]. 土壤通报, 1988, 19(2): 49-51. |
| YU T R. Acidity characteristics and acidification of soil in China[J]. Chinese Journal of Soil Science, 1988, 19(2): 49-51. | |
| [9] | 刘克豪. 红壤荒地的垦殖利用和改良熟化[J]. 土壤通报, 1963(4): 28-31. |
| LIU K H. Reclamation, utilization and improvement of red soil wasteland[J]. Chinese Journal of Soil Science, 1963(4): 28-31. | |
| [10] | 涂仕华. 化肥在农业可持续发展中的作用与地位[J]. 西南农业学报, 2003, 16(S1):7-11. |
| TU S H. Roles and functions of chemical fertilizers in sustainable agriculture[J]. Southwest China Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 2003, 16(S1):7-11. | |
| [11] | 熊毅, 陈家坊. 在农业生产大跃进中的土化肥问题[J]. 土壤, 1958(3): 1-2. |
| XIONG Y, CHEN J F. Problems of soil and fertilizer in the great leap forward of agricultural production[J]. Soils, 1958(3): 1-2. | |
| [12] | DONG Y, YANG J L, ZHAO X R, et al. Seasonal dynamics of soil pH and N transformation as affected by N fertilization in subtropical China: an in situ 15N labeling study[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2022, 816: 151596. |
| [13] | 杨帆, 贾伟, 杨宁, 等. 近30年我国不同地区农田耕层土壤的pH变化特征[J]. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2023, 29(7): 1213-1227. |
| YANG F, JIA W, YANG N, et al. Spatio-temporal variation of surface soil pH of farmland in different regions of China in the past 30 years[J]. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Fertilizers, 2023, 29(7): 1213-1227. | |
| [14] | 孙若梅. 化肥减量: 变化特征与“十四五” 目标的政策建议[J]. 农村经济, 2021(3): 1-8. |
| SUN R M. Fertilizer reduction: its changing characteristics and policy recommendations for objectives of “14th Five-Year Plan”[J]. Rural Economy, 2021(3): 1-8. | |
| [15] | 苗小红, 李志强. 工业化、城市化对耕地资源、质量与环境变化的影响[J]. 河南农业, 2008(21): 46. |
| MIAO X H, LI Z Q. Influence of industrialization and urbanization on cultivated land resources, quality and environmental changes[J]. Agriculture of Henan, 2008(21): 46. | |
| [16] | 余倩, 段雷, 郝吉明. 中国酸沉降: 来源、影响与控制[J]. 环境科学学报, 2021, 41(3): 731-746. |
| YU Q, DUAN L, HAO J M. Acid deposition in China: sources, effects and control[J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 2021, 41(3): 731-746. | |
| [17] | 王莉霞, 陈同斌, 宋波, 等. 广西环江流域硫污染农田的土壤酸化与酸性土壤分布[J]. 地理学报, 2008, 63(11): 1179-1188. |
| WANG L X, CHEN T B, SONG B, et al. Spatial distribution of acid soils in the Huanjiang river valley, Guangxi[J]. Acta Geographica Sinica, 2008, 63(11): 1179-1188. | |
| [18] | 郭剑辉. 工业废弃物对土壤的污染与防治[J]. 农业环境与发展, 1988, 5(1): 4-7. |
| GUO J H. Pollution of industrial waste to soil and its prevention and control[J]. Agro-Environment & Development, 1988, 5(1): 4-7. | |
| [19] | 周晓阳, 周世伟, 徐明岗, 等. 中国南方水稻土酸化演变特征及影响因素[J]. 中国农业科学, 2015, 48(23): 4811-4817. |
| ZHOU X Y, ZHOU S W, XU M G, et al. Evolution characteristics and influence factors of acidification in paddy soil of Southern China[J]. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 2015, 48(23): 4811-4817. | |
| [20] | 毛伟, 郁洁, 李文西, 等. 近40年江苏农田土壤pH时空变化特征及驱动因素[J]. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2023, 29(2): 264-272. |
| MAO W, YU J, LI W X, et al. Spatial and temporal variation of cropland pH and the driving factors in Jiangsu over the past 40 years[J]. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Fertilizers, 2023, 29(2): 264-272. | |
| [21] | 章明奎, 常跃畅. 近50年浙江省耕作土壤有机质和酸碱度的变化特征[J]. 环境科学, 2013, 34(11): 4399-4404. |
| ZHANG M K, CHANG Y C. Changing characteristics of organic matter and pH of cultivated soils in Zhejiang Province over the last 50 years[J]. Environmental Science, 2013, 34(11): 4399-4404. | |
| [22] | 曾招兵, 曾思坚, 刘一锋, 等. 1984年以来广东水稻土pH变化趋势及影响因素[J]. 土壤, 2014, 46(4): 732-736. |
| ZENG Z B, ZENG S J, LIU Y F, et al. Change tendency of paddy soil pH in Guangdong Province since 1984 and influential factors[J]. Soils, 2014, 46(4): 732-736. | |
| [23] | 孔德莉. 湖北省耕地土壤pH时空异质性及影响因素研究[D]. 武汉: 华中农业大学, 2021. |
| KONG D L. Spatiotemporal heterogeneity and influencing factors of soil pH in cultivated land in Hubei Province[D]. Wuhan: Huazhong Agricultural University, 2021. | |
| [24] | 龙泽东, 孙耿, 黄晶, 等. 近40年湖南省不同地区耕地土壤肥力变化特征[J]. 中国土壤与肥料, 2024(11): 37-48. |
| LONG Z D, SUN G, HUANG J, et al. Characteristics and variations of soil fertility in cultivated land across different regions of Hunan Province in the past 40 years[J]. Soil and Fertilizer Sciences in China, 2024(11): 37-48. | |
| [25] | 冯婧, 程兵芬, 王坤, 等. 我国西南地区典型降雨特征: 以贵州湄潭县为例[J]. 长江科学院院报, 2012, 29(12): 1-4. |
| FENG J, CHENG B F, WANG K, et al. Typical characteristics of rainfall evolution in southwest China: a case study of Meitan County in Guizhou Province[J]. Journal of Yangtze River Scientific Research Institute, 2012, 29(12): 1-4. | |
| [26] | LI Q Q, LI S, XIAO Y, et al. Soil acidification and its influencing factors in the purple hilly area of southwest China from 1981 to 2012[J]. CATENA, 2019, 175: 278-285. |
| [27] | WANG L, XIONG W Y, CHEN H, et al. Exploring the spatial distribution and influencing factors of soil pH value of cultivated land in Sichuan Province[J]. Environmental Earth Sciences, 2023, 83(1): 10. |
| [28] | 李金梅, 黄梅, 康吉利, 等. 1984—2019年广西土壤pH演变特征[J]. 生态学杂志, 2024, 43(11): 3317-3323. |
| LI J M, HUANG M, KANG J L, et al. The evolution characteristics of soil pH in Guangxi in 1984—2019[J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 2024, 43(11): 3317-3323. | |
| [29] | SHEN Y Y, ZHANG Z Q, XUE Y. Study on the new dynamics and driving factors of soil pH in the red soil, hilly region of South China[J]. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 2021, 193(5): 304. |
| [30] | 明雪, 康振威, 黄智刚. 广西扶绥县亚热带典型丘陵区耕地土壤pH的时空变异特征[J]. 西南农业学报, 2022, 35(1): 217-225. |
| MING X, KANG Z W, HUANG Z G. Temporal and spatial variation characteristics of cultivated soil pH in subtropical hilly region of Fusui County, Guangxi Province[J]. Southwest China Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 2022, 35(1): 217-225. | |
| [31] | 叶英聪, 孙波, 刘绍贵, 等. 中国水稻土酸化时空变化特征及其对氮素盈余的响应[J]. 农业机械学报, 2021, 52(2): 246-256. |
| YE Y C, SUN B, LIU S G, et al. Spatio-temporal variation of paddy soil acidification and its response to nitrogen surplus in China[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery, 2021, 52(2): 246-256. | |
| [32] | YANG Y H, JI C J, MA W H, et al. Significant soil acidification across northern China's grasslands during 1980s-2000s[J]. Global Change Biology, 2012, 18(7): 2292-2300. |
| [33] | 代钎里, 白银萍, 刘建亮, 等. 四川盆地近40年降雨量对耕层土壤pH时空变化的影响[J]. 西南农业学报, 2023, 36(5): 1019-1026. |
| DAI Q L, BAI Y P, LIU J L, et al. Influence of 40-year precipitation on temporal and spatial variation of arable soil pH in the Sichuan Basin[J]. Southwest China Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 2023, 36(5): 1019-1026. | |
| [34] | 汪吉东, 许仙菊, 宁运旺, 等. 土壤加速酸化的主要农业驱动因素研究进展[J]. 土壤, 2015, 47(4): 627-633. |
| WANG J D, XU X J, NING Y W, et al. Progresses in agricultural driving factors on accelerated acidification of soils[J]. Soils, 2015, 47(4): 627-633. | |
| [35] | GUO J H, LIU X J, ZHANG Y, et al. Significant acidification in major Chinese croplands[J]. Science, 2010, 327(5968): 1008-1010. |
| [36] | 马丽, 王青, 沈凇涛, 等. 岷江上游杂谷脑流域耕作区壤土和粉壤土的理化性质及肥力异质性[J]. 干旱区资源与环境, 2018, 32(11): 144-149. |
| MA L, WANG Q, SHEN S T, et al. The heterogeneity of physicochemical properties of cultivated soil and silt loam in Zagunao river basin, the upper Minjiang river[J]. Journal of Arid Land Resources and Environment, 2018, 32(11): 144-149. | |
| [37] | 王继红, 赵兰坡, 王宇, 等. 吉林省主要耕作土壤胶散复合体的组成特征[J]. 吉林农业大学学报, 2001, 23(3): 72-77. |
| WANG J H, ZHAO L P, WANG Y, et al. Study on the composition of organic-mineral complex of major cultivated soil from Jilin Province[J]. Journal of Jilin Agricultural University, 2001, 23(3): 72-77. | |
| [38] | 李少博, 徐英德, 高晓丹, 等. 离子界面行为在土壤有机无机复合体形成中的作用[J]. 中国生态农业学报, 2018, 26(11): 1682-1691. |
| LI S B, XU Y D, GAO X D, et al. The role of ionic interfacial behaviors in formation of soil organic-inorganic complexes[J]. Chinese Journal of Eco-Agriculture, 2018, 26(11): 1682-1691. | |
| [39] | XIE H H, WU Q G, HU J Y, et al. Changes in soil physical and chemical properties during the process of alpine meadow degradation along the eastern Qinghai-Tibet Plateau[J]. Eurasian Soil Science, 2018, 51(12): 1440-1446. |
| [40] | WEN Z, XU W, LI Q, et al. Changes of nitrogen deposition in China from 1980 to 2018[J]. Environment International, 2020, 144: 106022. |
| [41] | YU H L, HE N P, WANG Q F, et al. Development of atmospheric acid deposition in China from the 1990s to the 2010s[J]. Environmental Pollution, 2017, 231: 182-190. |
| [42] | WU Z F, SUN X M, SUN Y Q, et al. Soil acidification and factors controlling topsoil pH shift of cropland in central China from 2008 to 2018[J]. Geoderma, 2022, 408: 115586. |
| [43] | 郑梅迎, 林伟, 徐茜, 等. 基于CNKI数据库的土壤酸化文献计量分析[J]. 土壤, 2020, 52(4): 811-818. |
| ZHENG M Y, LIN W, XU Q, et al. Bibliometric analysis of soil acidification research based on CNKI database[J]. Soils, 2020, 52(4): 811-818. | |
| [44] | 韩天富, 柳开楼, 黄晶, 等. 近30年中国主要农田土壤pH时空演变及其驱动因素[J]. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2020, 26(12): 2137-2149. |
| HAN T F, LIU K L, HUANG J, et al. Spatio-temporal evolution of soil pH and its driving factors in the main Chinese farmland during past 30 years[J]. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Fertilizers, 2020, 26(12): 2137-2149. | |
| [45] | ZHU Q C, DE VRIES W, LIU X J, et al. The contribution of atmospheric deposition and forest harvesting to forest soil acidification in China since 1980[J]. Atmospheric Environment, 2016, 146: 215-222. |
| [46] | RAZA S, MIAO N, WANG P Z, et al. Dramatic loss of inorganic carbon by nitrogen-induced soil acidification in Chinese croplands[J]. Global Change Biology, 2020, 26(6): 3738-3751. |
| [47] | TIAN D S, NIU S L. A global analysis of soil acidification caused by nitrogen addition[J]. Environmental Research Letters, 2015, 10(2): 024019. |
| [48] | 闫湘, 金继运, 梁鸣早. 我国主要粮食作物化肥增产效应与肥料利用效率[J]. 土壤, 2017, 49(6): 1067-1077. |
| YAN X, JIN J Y, LIANG M Z. Fertilizer use efficiencies and yield-increasing rates of grain crops in China[J]. Soils, 2017, 49(6): 1067-1077. | |
| [49] | 刘钦普, 孙景荣, 濮励杰. 中国及欧美主要国家化肥施用强度与综合效率比较研究[J]. 农业工程学报, 2020, 36(14): 9-16. |
| LIU Q P, SUN J R, PU L J. Comparative study on fertilization intensity and integrated efficiency in China and Euro-American major countries[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 2020, 36(14): 9-16. | |
| [50] | 徐仁扣, 李九玉, 周世伟, 等. 我国农田土壤酸化调控的科学问题与技术措施[J]. 中国科学院院刊, 2018, 33(2): 160-167. |
| XU R K, LI J Y, ZHOU S W, et al. Scientific issues and controlling strategies of soil acidification of croplands in China[J]. Bulletin of Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2018, 33(2): 160-167. | |
| [51] | WANG Z, TAO T T, WANG H, et al. Forms of nitrogen inputs regulate the intensity of soil acidification[J]. Global Change Biology, 2023, 29(14): 4044-4055. |
| [52] | LIU L, WEN Z, LIU S, et al. Decline in atmospheric nitrogen deposition in China between 2010 and 2020[J]. Nature Geoscience, 2024, 17(8): 733-736. |
| [53] | 鲁如坤. 施用石灰的原理浅说[J]. 农业科学通讯, 1956(11): 684-685. |
| LU R K. On the principle of applying lime[J]. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 1956(11): 684-685. | |
| [54] | 李庆逵. 关于红壤改良的研究[J]. 土壤通报, 1959(5): 3-8. |
| LI Q K. Study on improvement of red soil[J]. Chinese Journal of Soil Science, 1959(5): 3-8. | |
| [55] | 裴德安. 江西对红壤改良利用的主要经验[J]. 土壤, 1959(10): 31-32. |
| PEI D A. Jiangxi's main experience in improving and utilizing red soil[J]. Soils, 1959(10): 31-32. | |
| [56] | 吕侠卿. 湖南邵东大力子丰产经验[J]. 中国药学杂志, 1959(8): 383. |
| LYU X Q. High-yield experience of dalizi in Shaodong, Hunan Province[J]. Chinese Pharmaceutical Journal, 1959(8): 383. | |
| [57] | 中国科学院土壤研究所孝感工作组. 湖北孝感县水稻丰产区深耕深翻的群众经验总结[J]. 土壤, 1959(2): 11-14. |
| Xiaogan Working Group, Institute of Soil Science, Chinese Academy of Sciences. Summary of the experience of deep ploughing and deep ploughing in the high-yield rice area of Xiaogan County, Hubei Province[J]. Soils, 1959(2): 11-14. | |
| [58] | 肖恕贤. 广西农民对水稻的几种合理施肥法[J]. 土壤, 1959(11): 29-30. |
| XIAO S X. Several rational fertilization methods for rice by farmers in Guangxi[J]. Soils, 1959(11): 29-30. | |
| [59] | 熊欢全. 施用石灰的经验及对改良土壤的效果[J]. 土壤, 1959(2): 20-17. |
| XIONG H Q. Experience of applying lime and its effect on improving soil[J]. Soils, 1959(2): 20-17. | |
| [60] | 金格里П А, 管绍淳. 马尔采夫土壤耕作法的科学基础[J]. 科学通报, 1955(2): 56-58. |
| KINGRY Π А, GUAN S C. Scientific basis of soil tillage method in Malcev[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 1955(2): 56-58. | |
| [61] | 刘春林. 灌溉和排水为什么能增进土壤肥力[J]. 中国水利, 1962(17): 27-28. |
| LIU C L. Why irrigation and drainage can improve soil fertility[J]. China Water Resources, 1962(17): 27-28. | |
| [62] | 孟世福, 水建国. 红壤施用石灰石粉对作物产量和土壤化学性质的影响[J]. 浙江农业科学, 1982, 23(5): 253-257. |
| MENG S F, SHUI J G. Effects of limestone powder on crop yield and soil chemical properties in red soil[J]. Journal of Zhejiang Agricultural Science, 1982, 23(5): 253-257. | |
| [63] | DELFIM J, MOREIRA A, MORAES L A C. Wheat growth, yield, nutrient concentration and soil chemical properties influenced by liming in an acid soil[J]. Journal of Plant Nutrition, 2025, 48(1): 87-100. |
| [64] | KEIBLINGER K M, BAUER L M, DELTEDESCO E, et al. Quicklime application instantly increases soil aggregate stability[J]. International Agrophysics, 2016, 30(1): 123-128. |
| [65] | BORTOLUZZI E C, GARBOZZA L, GUARESCHI C, et al. Efeito da calagem na relação entre solo e água[J]. Revista Brasileira de Ciência Do Solo, 2008, 32: 2621-2628. |
| [66] | 胡敏, 向永生, 鲁剑巍. 石灰用量对酸性土壤pH值及有效养分含量的影响[J]. 中国土壤与肥料, 2017(4): 72-77. |
| HU M, XIANG Y S, LU J W. Effects of lime application rates on soil pH and available nutrient content in acidic soils[J]. Soil and Fertilizer Sciences in China, 2017(4): 72-77. | |
| [67] | BRENNAN R F, BOLLAND M D A, BELL R W. Increased risk of zinc deficiency in wheat on soils limed to correct soil acidity[J]. Soil Research, 2005, 43(5): 647-657. |
| [68] | WEST T O, MCBRIDE A C. The contribution of agricultural lime to carbon dioxide emissions in the United States: dissolution, transport, and net emissions[J]. Agriculture, Ecosystems & Environment, 2005, 108(2): 145-154. |
| [69] | 郭熙盛. 利用白云石改良皖南酸性旱地红黄壤[J]. 安徽农业, 2002(10): 27. |
| GUO X S. Improvement of red and yellow soil in acid dry land in southern Anhui by dolomite[J]. Anhui Agriculture, 2002(10): 27. | |
| [70] | 何佳芳, 肖厚军, 芶久兰. 磷石膏与沸石对酸性黄壤活性铝形态及作物营养平衡的影响[J]. 西南农业学报, 2009, 22(3): 727-732. |
| HE J F, XIAO H J, GOU J L. Effects of phosphogypsum and zeolite on active aluminium form in acidic yellow soil and nutrient balance of carrot[J]. Southwest China Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 2009, 22(3): 727-732. | |
| [71] | 王振荣. 磷矿粉改良咸酸田的效果[J]. 土壤, 1980, 12(4): 145-147. |
| WANG Z R. Effect of phosphate rock powder on improving saline-acid field[J]. Soils, 1980, 12(4): 145-147. | |
| [72] | 吴家华, 刘宝山, 董云中, 等. 粉煤灰改土效应研究[J]. 土壤学报, 1995, 32(3):334-340. |
| WU J H, LIU B S, DONG Y Z, et al. Study on effect of soil amelioration with coal ash[J]. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 1995, 32(3):334-340. | |
| [73] | 廖宗文, 何振富, 冯粉红. 两种工业废料对咸酸田改良效果的初步研究[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 1991, 10(3): 105-107, 145. |
| LIAO Z W, HE Z F, FENG F H. A preliminary study of amelioration effect of two kinds of industrial wastes on acid sulphur soil[J]. Journal of Agro-Environmental Science, 1991, 10(3): 105-107, 145. | |
| [74] | 李九玉, 王宁, 徐仁扣. 工业副产品对红壤酸度改良的研究[J]. 土壤, 2009, 41(6): 932-939. |
| LI J Y, WANG N, XU R K. Amelioration of industrial by-products on soil acidity in red soil[J]. Soils, 2009, 41(6): 932-939. | |
| [75] | ZOCA S M, PENN C. An important tool with no instruction manual[M]//Advances in agronomy. Amsterdam: Elsevier, 2017: 1-44. |
| [76] | 冯敬云, 聂新星, 刘波, 等. 镉污染农田原位钝化修复效果及其机理研究进展[J]. 农业资源与环境学报, 2021, 38(5): 764-777. |
| FENG J Y, NIE X X, LIU B, et al. Efficiency of in situ passivation remediation in cadmium-contaminated farmland soil and its mechanism: a review[J]. Journal of Agricultural Resources and Environment, 2021, 38(5): 764-777. | |
| [77] | 柴有忠, 张圆圆, 马军伟, 等. 不同酸性改良剂对葡萄园土壤及葡萄品质的影响[J]. 中国土壤与肥料, 2021(2): 102-107. |
| CHAI Y Z, ZHANG Y Y, MA J W, et al. Effects of different acid conditioners on soil and grape quality[J]. Soil and Fertilizer Sciences in China, 2021(2): 102-107. | |
| [78] | 刘玉学, 吕豪豪, 石岩, 等. 生物质炭对土壤养分淋溶的影响及潜在机理研究进展[J]. 应用生态学报, 2015, 26(1): 304-310. |
| LIU Y X, LYU H H, SHI Y, et al. Effects of biochar on soil nutrients leaching and potential mechanisms: a review[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2015, 26(1): 304-310. | |
| [79] | 俞巧钢, 孙万春, 叶静, 等. 有机肥替代化肥对橘园土壤培肥及果实产量品质的影响[J]. 农业资源与环境学报, 2023, 40(4): 755-762. |
| YU Q G, SUN W C, YE J, et al. Effects of organic manure substituting chemical fertilizer on soil fertility and fruit yield and quality in Citrus orchard[J]. Journal of Agricultural Resources and Environment, 2023, 40(4): 755-762. | |
| [80] | 吴宇凡, 王鸿睿, 樊浩杰, 等. 海藻寡糖在绿色农业发展中的研究与应用[J]. 中国农学通报, 2024, 40(17): 63-72. |
| WU Y F, WANG H R, FAN H J, et al. Research and application of seaweed oligosaccharides in the development of green agriculture[J]. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin, 2024, 40(17): 63-72. | |
| [81] | 李玮琳, 张昕, 马军伟, 等. 抗生素降解菌剂对猪粪堆肥腐熟和细菌群落演替的影响[J]. 环境科学, 2022, 43(10): 4789-4800. |
| LI W L, ZHANG X, MA J W, et al. Effect of antibiotic-degrading bacteria on maturity and bacterial community succession during pig manure composting[J]. Environmental Science, 2022, 43(10): 4789-4800. | |
| [82] | 俞巧钢, 姜铭北, 孙万春, 等. 秸秆覆盖和绿肥种植对丘陵茶园氮磷流失的影响[J]. 浙江农业学报, 2023, 35(4): 903-912. |
| YU Q G, JIANG M B, SUN W C, et al. Effects of straw mulching and green manure planting on nitrogen and phosphorus runoff loss in hilly tea garden[J]. Acta Agriculturae Zhejiangensis, 2023, 35(4): 903-912. | |
| [83] | 温炜, 潘建清, 俞波, 等. 长兴县葡萄耕地主推酸化治理模式应用效果研究[J]. 浙江农业科学, 2024, 65(8): 1838-1842. |
| WEN W, PAN J Q, YU B, et al. Study on the application effect of the main acidification management model for grape cultivated land in Changxing County[J]. Journal of Zhejiang Agricultural Sciences, 2024, 65(8): 1838-1842. | |
| [84] | 陈惠英, 王峰, 王强, 等. 新垦耕地土壤肥力提升路径探析: 以浙江省为例[J]. 中国农学通报, 2023, 39(18): 75-80. |
| CHEN H Y, WANG F, WANG Q, et al. Analysis of soil fertility improvement path of newly reclaimed cultivated land: a case study in Zhejiang Province[J]. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin, 2023, 39(18): 75-80. |
| [1] | 朱玉祥, 陈佳毅, 费徐峰, 吴勇, 任周桥. 桐乡市耕地质量时空变动及驱动因素[J]. 浙江农业科学, 2026, 67(1): 194-201. |
| [2] | 徐洁章, 叶陈帅, 周卿伟, 吴卫红, 童晓翠. 浙中低山丘陵区土壤肥力特征研究[J]. 浙江农业科学, 2025, 66(9): 2271-2279. |
| [3] | 殷贝贝, 黄金生, 王磊, 周柳强, 朱晓晖, 彭嘉宇, 谢如林, 曾艳, 区惠平, 李忠宁, 卢红媚, 莫文彬, 何冬秋, 刘利君, 张宪. 广西茶园土壤酸度与交换性氢、铝的关系[J]. 浙江农业科学, 2025, 66(6): 1349-1354. |
| [4] | 郭爱环, 练青平, 张爱菊, 陈伟, 陈欢, 盛鹏程, 原居林, 陈光美. 千峡湖水库浮游动物种群变化特征及其关键驱动因子研究[J]. 浙江农业科学, 2025, 66(10): 2478-2486. |
| [5] | 温炜, 潘建清, 俞波, 解静, 马军伟, 杨艳, 王峰. 长兴县葡萄耕地主推酸化治理模式应用效果研究[J]. 浙江农业科学, 2024, 65(8): 1838-1842. |
| [6] | 项舒延, 詹丽钏, 周卿伟, 金美青, 吴卫红, 傅力. 不同植茶年份土壤性质差异研究[J]. 浙江农业科学, 2024, 65(6): 1364-1369. |
| [7] | 李梦妮, 吴鲁洁, 赵觅漾, 陈翰, 卢升高. 土壤调理剂阻控土壤酸化提高磷素养分有效性的田间对比试验[J]. 浙江农业科学, 2024, 65(12): 2899-2905. |
| [8] | 胡文君, 游春燕, 牛二利, 俞春莲, 王昆喜, 朱春权, 卢红伶, 蒋陈凯, 陈琳, 蒋起宏, 凌楸桐, 朱申龙, 郑海雷, 沈国新. 土壤酸化条件下植物响应铝毒时钙与铝交互作用的研究进展[J]. 浙江农业科学, 2024, 65(12): 3048-3052. |
| [9] | 王勤俭, 王峰, 俞巧钢, 刘海天, 杨艳, 柴有忠, 张圆圆, 马军伟. 不同土壤调理剂对红黄壤黄桃园土壤及黄桃品质的影响[J]. 浙江农业科学, 2022, 63(8): 1743-1747. |
| [10] | 童文彬, 江建锋, 杨海峻, 陈喜靖, 林义成, 刘琛, 张露华, 方俊, 郭彬. 南方典型酸化土壤改良与水稻安全种植同步应用技术[J]. 浙江农业科学, 2022, 63(6): 1154-1156. |
| [11] | 吴林土, 徐火忠, 李贵松, 唐仕琴, 王勇军. 微生物菌剂对松阳茶园土壤酸化改良及肥力提升的效果分析[J]. 浙江农业科学, 2022, 63(6): 1245-1249. |
| [12] | 宋洋, 刘冬峰, 赵泉, 郭秀珠, 李发勇, 林绍生. 不同镁肥对柚园土壤和树体营养的影响[J]. 浙江农业科学, 2022, 63(6): 1275-1278. |
| [13] | 赵丽芳, 黄鹏武, 陈翰, 卢升高. 土壤调理剂与有机肥配施治理红壤茶园土壤酸化与培育地力的效果[J]. 浙江农业科学, 2022, 63(11): 2692-2695. |
| [14] | 周杨, 姚岳良, 施丽珍, 陈建霞, 章明奎. 缙云县耕地土壤酸化及其预防与治理思考[J]. 浙江农业科学, 2021, 62(4): 833-836. |
| [15] | 鲍莹, 张安明. 重庆合川区土地利用碳排放的效应及驱动因素[J]. 浙江农业科学, 2021, 62(2): 440-444. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||