
浙江农业科学 ›› 2026, Vol. 67 ›› Issue (1): 184-193.DOI: 10.16178/j.issn.0528-9017.20240822
胡绮琪1,2( ), 梁嘉伟2, 余炜敏2, 王荣萍2,*(
), 梁嘉伟2, 余炜敏2, 王荣萍2,*( ), 龚贝妮1, 林壁润3
), 龚贝妮1, 林壁润3
收稿日期:2024-10-25
出版日期:2026-01-11
发布日期:2026-01-19
通讯作者:
王荣萍
作者简介:王荣萍,E-mail:rpwang@soil.gd.cn。基金资助:
HU Qiqi1,2( ), LIANG Jiawei2, YU Weimin2, WANG Rongping2,*(
), LIANG Jiawei2, YU Weimin2, WANG Rongping2,*( ), GONG Beini1, LIN Birun3
), GONG Beini1, LIN Birun3
Received:2024-10-25
Online:2026-01-11
Published:2026-01-19
Contact:
WANG Rongping
摘要:
本研究以根际土壤为研究对象,设置菜心-玉米轮作与非轮作处理,分析土壤有机质含量、土壤有效磷含量、土壤微生物生物量磷(SMBP)含量、土壤酸性磷酸酶活性和土壤微生物生物量碳(SMBC)含量在轮作周期内的变化,并采用Pearson法分析各指标间的相关性。结果表明,菜心-玉米轮作处理的根际土壤有机质含量、有效磷含量、SMBP含量与酸性磷酸酶活性在作物种植期均显著(p<0.05)高于非轮作处理,SMBC/SMBP均低于非轮作处理,比值在30以下。土壤有效磷含量与SMBP含量、土壤酸性磷酸酶活性、土壤SMBC含量和土壤有机质含量之间呈极显著(p<0.01)正相关,相关系数分别达0.869、0.815、0.611与0.441,与SMBC/SMBP和土壤pH值呈显著负相关关系,相关系数分别达-0.397与-0.850。轮作显著激活土壤磷素循环,促进作物对土壤中磷素的利用,实现养分的平衡吸收,兼顾农业生产与土壤培育。
中图分类号:
胡绮琪, 梁嘉伟, 余炜敏, 王荣萍, 龚贝妮, 林壁润. 菜心-玉米轮作对根际土壤微生物生物量及酶活性的影响[J]. 浙江农业科学, 2026, 67(1): 184-193.
HU Qiqi, LIANG Jiawei, YU Weimin, WANG Rongping, GONG Beini, LIN Birun. Effects of Brassica campestris var. parachinensis-maize rotation on microbial biomass and enzyme activity in rhizosphere soil[J]. Journal of Zhejiang Agricultural Sciences, 2026, 67(1): 184-193.
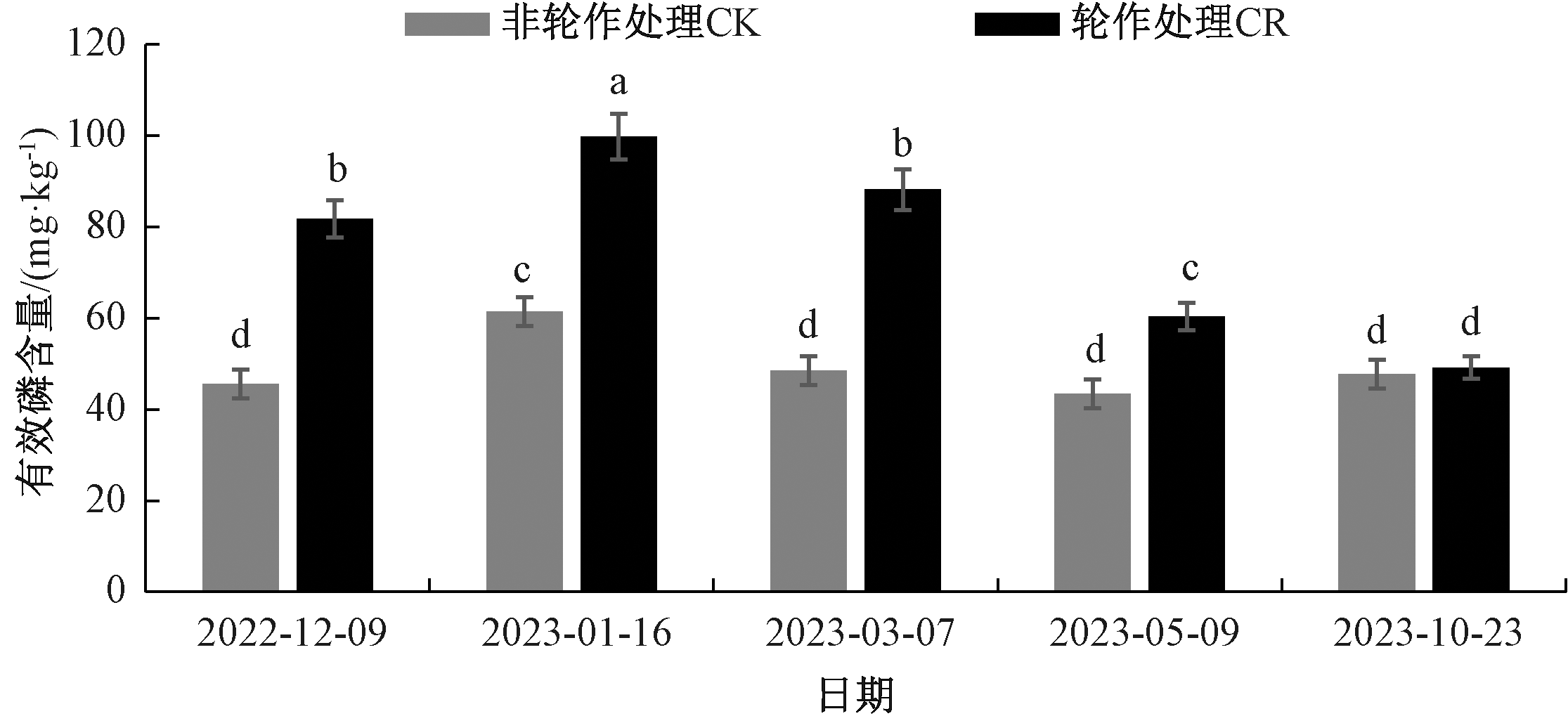
图1 轮作与非轮作处理下根际土壤的有效磷含量 柱上无相同小写字母表示不同处理间差异显著(p<0.05),图2~6同。
Fig.1 Available phosphorus content in rhizosphere soil under rotation and non-rotation treatments
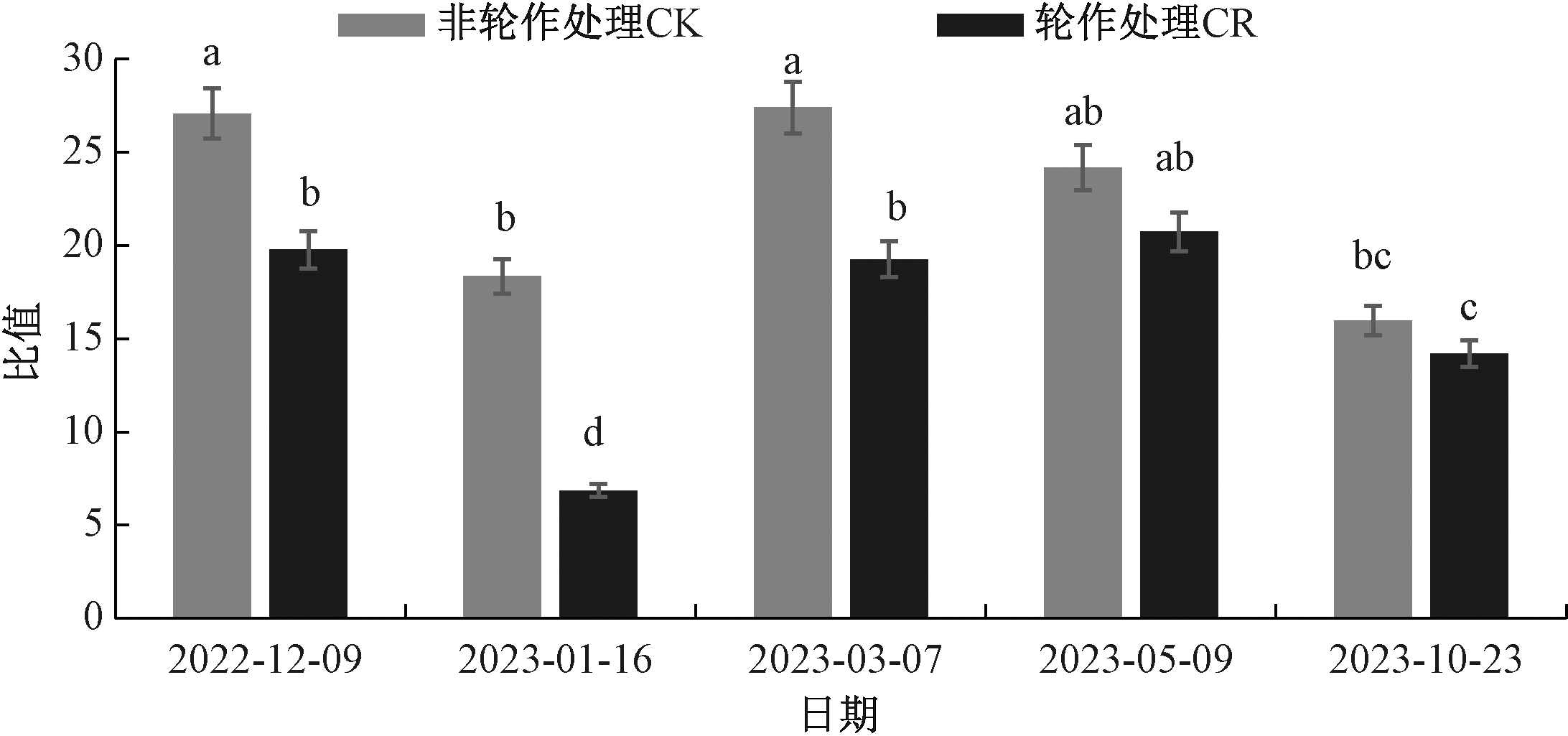
图5 轮作与非轮作处理下根际土壤微生物生物量碳与微生物生物量磷含量的比值
Fig.5 The ratio of microbial biomass carbon content and microbial biomass phosphorus content in rhizosphere soil under rotation and non-rotation treatments
| 指标 | 土壤pH值 | 土壤有机 质含量 | 土壤有效 磷含量 | 土壤微生物生物量 磷(SMBP)含量 | 酸性磷酸 酶活性 | 土壤微生物生物量碳与 土壤微生物生物量 磷含量的比值 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 土壤有机质含量 | -0.539** | |||||
| 土壤有效磷含量 | -0.850** | 0.441** | ||||
| 土壤微生物生物量磷(SMBP)含量 | -0.741** | 0.526** | 0.869** | |||
| 酸性磷酸酶活性 | -0.877** | 0.679** | 0.815** | 0.715** | ||
| 土壤微生物生物量碳与土壤微生物生物量磷含量的比值(SMBC/SMBP) | 0.273 | -0.248 | -0.397* | -0.565** | -0.275 | |
| 土壤微生物生物量碳(SMBC)含量 | -0.648** | 0.533** | 0.611** | 0.176 | 0.753** | 0.310 |
表1 土壤pH值、有机质含量、有效磷含量、酸性磷酸酶活性与土壤微生物生物量的相关性分析
Table 1 Correlation between soil pH value, organic matter content, available phosphorus content, acid phosphatase activity and soil microbial biomass
| 指标 | 土壤pH值 | 土壤有机 质含量 | 土壤有效 磷含量 | 土壤微生物生物量 磷(SMBP)含量 | 酸性磷酸 酶活性 | 土壤微生物生物量碳与 土壤微生物生物量 磷含量的比值 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 土壤有机质含量 | -0.539** | |||||
| 土壤有效磷含量 | -0.850** | 0.441** | ||||
| 土壤微生物生物量磷(SMBP)含量 | -0.741** | 0.526** | 0.869** | |||
| 酸性磷酸酶活性 | -0.877** | 0.679** | 0.815** | 0.715** | ||
| 土壤微生物生物量碳与土壤微生物生物量磷含量的比值(SMBC/SMBP) | 0.273 | -0.248 | -0.397* | -0.565** | -0.275 | |
| 土壤微生物生物量碳(SMBC)含量 | -0.648** | 0.533** | 0.611** | 0.176 | 0.753** | 0.310 |
| [1] | 赵其国, 滕应, 黄国勤. 中国探索实行耕地轮作休耕制度试点问题的战略思考[J]. 生态环境学报, 2017, 26(1): 1-5. |
| ZHAO Q G, TENG Y, HUANG G Q. Consideration about exploring pilot program of farmland rotation and fallow system in China[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 2017, 26(1): 1-5. | |
| [2] | 郭树健, 李淑娟, 李娜, 等. 红壤旱地以玉米为主体的不同种植模式对土壤碳库管理指数的影响[J]. 华中农业大学学报, 2022, 41(6): 128-136. |
| GUO S J, LI S J, LI N, et al. Effects of different planting patterns with maize as the main body on index of carbon pool management in red soil dryland[J]. Journal of Huazhong Agricultural University, 2022, 41(6): 128-136. | |
| [3] | 杨凤娟, 吴焕涛, 魏珉, 等. 轮作与休闲对日光温室黄瓜连作土壤微生物和酶活性的影响[J]. 应用生态学报, 2009, 20(12): 2983-2988. |
| YANG F J, WU H T, WEI M, et al. Effects of rotation and fallowing on the microbial communities and enzyme activities in a solar greenhouse soil under continuous cucumber cropping[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2009, 20(12): 2983-2988. | |
| [4] | 张科, 袁玲, 施娴, 等. 不同植烟模式对烤烟产质量、土壤养分和酶活性的影响[J]. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2010, 16(1): 124-128. |
| ZHANG K, YUAN L, SHI X, et al. Effects of cropping patterns on yield and quality of flue-cured tobacco, soil nutrients and enzyme activities[J]. Plant Nutrition and Fertilizer Science, 2010, 16(1): 124-128. | |
| [5] | 邵兴华, RICHARD D. 土壤化学特性、酶活性和产量对农业措施的敏感性研究[J]. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2021, 27(12): 2105-2113. |
| SHAO X H, RICHARD D. Study on the sensitivity of soil chemical properties, enzyme activities and yield to agricultural measures[J]. Plant Nutrition and Fertilizer Science, 2021, 27(12): 2105-2113. | |
| [6] | 赵仰徽, 齐向辉, 任稳江, 等. 半干旱区雨养农田绿肥作物轮作休耕技术措施研究[J]. 干旱区资源与环境, 2024, 38(1): 123-132. |
| ZHAO Y H, QI X H, REN W J, et al. An approach to green manure crop rotation fallow technigues for rainfed farmland in semi-arid areas[J]. Journal of Arid Land Resources and Environment, 2024, 38(1): 123-132. | |
| [7] | 牛昱涵, 施曼, 王心怡, 等. 苏南地区农业土地利用方式改变对土壤理化及生物学性质的影响[J]. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2019, 25(10): 1657-1668. |
| NIU Y H, SHI M, WANG X Y, et al. Influence of agricultural land use changes on soil physiochemical and biological characteristics in Southern Jiangsu Province[J]. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Fertilizers, 2019, 25(10): 1657-1668. | |
| [8] | 鲁连欣, 王克勤, 李珠宇, 等. 等高反坡台阶整地对不同耕作系统根土微生态的影响[J]. 水土保持学报, 2024, 38(2): 326-338. |
| LU L X, WANG K Q, LI Z Y, et al. Effects of contour reverse-slope terrace on the microecology of rhizosphere in different farming systems[J]. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 2024, 38(2): 326-338. | |
| [9] | 蒋如, 宁诗琪, 隋宗明, 等. 长期轮作施肥处理对植烟土壤有机碳组分和酶活性的影响[J]. 土壤, 2024, 56(3): 510-516. |
| JIANG R, NING S Q, SUI Z M, et al. Effects of long-term rotation and fertilization treatments on organic carbon fractions and enzyme activities in tobacco-planting soil[J]. Soils, 2024, 56(3): 510-516. | |
| [10] | 吴杨潇影, 姜振辉, 杨京平, 等. 玉米-水稻轮作和水稻连作土壤根际和非根际氮含量及酶活性[J]. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2019, 25(4): 535-543. |
| WU Y, JIANG Z H, YANG J P, et al. Nitrogen content and enzyme activity in rhizosphere and non-rhizosphere soils of paddy field under maize-rice rotation and rice continuous mono-cropping[J]. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Fertilizers, 2019, 25(4): 535-543. | |
| [11] | 袁海燕, 袁汉民, 赵万伏, 等. 多年麦稻轮作免耕土壤细菌对土壤养分和酶活性的影响[J]. 中国土壤与肥料, 2023(11): 50-59. |
| YUAN H Y, YUAN H M, ZHAO W F, et al. The soil bacteria could improve soil nutrient and enzyme activity under wheat rice rotation and zero-tillage for continuous years[J]. Soils and Fertilizers Sciences in China, 2023(11): 50-59. | |
| [12] | 赵峥, 朱元宏, 周德平, 等. 不同轮作模式对稻田土壤肥力和微生物群落结构的影响[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2024, 43(4): 874-885. |
| ZHAO Z, ZHU Y H, ZHOU D P, et al. Effects of different rotation patterns on soil fertility and microbial community composition in a paddy field system[J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 2024, 43(4): 874-885. | |
| [13] | 李洪亮, 诸海焘, 徐四新, 等. 碳对微生物-根系介导的蔬菜作物磷吸收的影响[J]. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2021, 27(10): 1757-1766. |
| LI H L, ZHU H T, XU S X, et al. Effects of carbon on microbe-root interaction mediating P acquisition by vegetable crops[J]. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Fertilizers, 2021, 27(10): 1757-1766. | |
| [14] | 苟小梅, 王昌全, 李冰, 等. 玉米种植制度对红壤磷素形态及其有效性的影响[J]. 应用生态学报, 2020, 31(3): 883-889. |
| GOU X M, WANG C Q, LI B, et al. Effects of corn-based cropping systems on phosphorus fractions and availability in red soil[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 2020, 31(3): 883-889. | |
| [15] | 鲁如坤. 土壤农业化学分析方法[M]. 北京: 中国农业科学技术出版社, 2000. |
| [16] | 林先贵. 土壤微生物研究原理与方法[M]. 北京: 高等教育出版社, 2010. |
| [17] | HEUCK C, WEIG A, SPOHN M. Soil microbial biomass C: N: P stoichiometry and microbial use of organic phosphorus[J]. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 2015, 85: 119-129. |
| [18] | 杨梦棣, 赵萍萍, 于志勇, 等. 晋南地区小麦-玉米轮作体系维持作物高产和土壤磷素水平的适宜施磷量研究[J]. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2022, 28(3): 440-449. |
| YANG M D, ZHAO P P, YU Z Y, et al. Optimum phosphorus application rate for maintaining high yield and soil phosphorus fertility under winter wheat-summer maize rotation in Shanxi Province[J]. Plant Nutrition and Fertilizer Science, 2022, 28(3): 440-449. | |
| [19] | EBHIN MASTO R, CHHONKAR P K, SINGH D, et al. Changes in soil biological and biochemical characteristics in a long-term field trial on a sub-tropical inceptisol[J]. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 2006, 38(7): 1577-1582. |
| [20] | 曾晓敏, 高金涛, 范跃新, 等. 中亚热带森林转换对土壤磷积累的影响[J]. 生态学报, 2018, 38(13): 4879-4887. |
| ZENG X M, GAO J T, FAN Y X, et al. Effect of soil factors after forest conversion on the accumulation of phosphorus species in mid-subtropical forests[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2018, 38(13): 4879-4887. | |
| [21] | 令狐荣云, 王荣萍, 梁嘉伟, 等. 铁还原菌对红壤菜地土壤磷形态转化的影响[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2016, 35(9): 1742-1749. |
| LINGHU R Y, WANG R P, LIANG J W, et al. Effects of Iron-reducing bacteria on the transformation of phosphorus in vegetable red soils[J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 2016, 35(9): 1742-1749. | |
| [22] | 薛冬, 姚槐应, 黄昌勇. 植茶年龄对茶园土壤微生物特性及酶活性的影响[J]. 水土保持学报, 2005, 19(2): 84-87. |
| XUE D, YAO H Y, HUANG C Y. Study on soil microbial properties and enzyme activities in tea gardens[J]. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 2005, 19(2): 84-87. | |
| [23] | CHEN C R, CONDRON L M, DAVIS M R, et al. Seasonal changes in soil phosphorus and associated microbial properties under adjacent grassland and forest in New Zealand[J]. Forest Ecology and Management, 2003, 177(1/2/3): 539-557. |
| [24] | KATSALIROU E, DENG S P, GERAKIS A, et al. Long-term management effects on soil P, microbial biomass P, and phosphatase activities in prairie soils[J]. European Journal of Soil Biology, 2016, 76: 61-69. |
| [25] | 朱广鹏. 猪粪施用对黑土水稻土淹水-落干过程磷转化影响及微生物响应研究[D]. 沈阳: 沈阳师范大学, 2023. |
| ZHU G P. Effects of pig manure application and flooding-drying on phosphorus conversion and microbial response in paddy soil of black area[D]. Shenyang: Shenyang Normal University, 2023. | |
| [26] | 李炎龙, 季荣博, 吴云, 等. 我国北方3种典型土壤-作物体系中微生物量磷库特征[J]. 生态学报, 2022, 42(8): 3325-3332. |
| LI Y L, JI R B, WU Y, et al. Soil microbial biomass phosphorus pool in farmlands of the Northern China[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2022, 42(8): 3325-3332. | |
| [27] | KOUNO K, WU J, BROOKES P C. Turnover of biomass C and P in soil following incorporation of glucose or ryegrass[J]. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 2002, 34(5): 617-622. |
| [28] | CHEN H, ZHAO X R, CHEN X J, et al. Seasonal changes of soil microbial C, N, P and associated nutrient dynamics in a semiarid grassland of North China[J]. Applied Soil Ecology, 2018, 128: 89-97. |
| [29] | 李丹丹, 彭懿, 冯固, 等. 洱海流域高肥力土壤的碳磷比特征及调控途径[J]. 水土保持学报, 2023, 37(6): 255-261. |
| LI D D, PENG Y, FENG G, et al. Characteristics of C∶P ratio in high fertility soil in Erhai Lake Basin and its regulation approach[J]. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 2023, 37(6): 255-261. | |
| [30] | VAN DER HEIJDEN M G A, BARDGETT R D, VAN STRAALEN N M. The unseen majority: soil microbes as drivers of plant diversity and productivity in terrestrial ecosystems[J]. Ecology Letters, 2008, 11(3): 296-310. |
| [31] | MARTIN-LAURENT F, BARRÈS B, WAGSCHAL I, et al. Impact of the maize rhizosphere on the genetic structure, the diversity and the atrazine-degrading gene composition of cultivable atrazine-degrading communities[J]. Plant and Soil, 2006, 282(1): 99-115. |
| [32] | 冯瑞章, 周万海, 龙瑞军, 等. 江河源区不同退化程度高寒草地土壤物理、化学及生物学特征研究[J]. 土壤通报, 2010, 41(2): 263-269. |
| FENG R Z, ZHOU W H, LONG R J, et al. Characteristics of soil physical, chemical and biological properties on degraded alpine meadows in the headwater areas of the Yangtze and Yellow Rivers, Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau[J]. Chinese Journal of Soil Science, 2010, 41(2): 263-269. | |
| [33] | 黄宇, 张海伟, 徐芳森. 植物酸性磷酸酶的研究进展[J]. 华中农业大学学报, 2008(1): 148-154. |
| HUANG Y, ZHANG H W, XU F S. Research progress on plant acid phosphatase[J]. Journal of Huazhong Agricultural University, 2008(1): 148-154. | |
| [34] | HOU E Q, CHEN C R, WEN D Z, et al. Phosphatase activity in relation to key litter and soil properties in mature subtropical forests in China[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2015, 515/516: 83-91. |
| [35] | SINSABAUGH R L, FOLLSTAD SHAH J J. Ecoenzymatic stoichiometry and ecological theory[J]. Annual Review of Ecology, Evolution, and Systematics, 2012, 43: 313-343. |
| [36] | 王宏生, 王玉琴, 宋梅玲, 等. 黄帚橐吾不同密度斑块植物、土壤和微生物碳氮磷生态化学计量特征[J]. 生态学报, 2024, 44(10): 4297-4307. |
| WANG H S, WANG Y Q, SONG M L, et al. Carbon, nitrogen and phosphorus stoichiometric characteristics of plants, soils and microbial biomass in patches with different densities of Ligularia virgaurea[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2024, 44(10): 4297-4307. | |
| [37] | 王传杰, 肖婧, 蔡岸冬, 等. 不同气候与施肥条件下农田土壤微生物生物量特征与容量分析[J]. 中国农业科学, 2017, 50(6): 1067-1075. |
| WANG C J, XIAO J, CAI A D, et al. Capacity and characteristics of soil microbial biomass under various climate and fertilization conditions across China croplands[J]. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 2017, 50(6): 1067-1075. | |
| [38] | 王理德, 王方琳, 郭春秀, 等. 土壤酶学硏究进展[J]. 土壤, 2016, 48(1): 12-21. |
| WANG L D, WANG F L, GUO C X, et al. Review: progress of soil enzymology[J]. Soils, 2016, 48(1): 12-21. | |
| [39] | 张福锁, 曹一平. 根际动态过程与植物营养[J]. 土壤学报, 1992, 29(3): 239-250. |
| ZHANG F S, CAO Y P. Rhizosphere dynamics and plant nutrition[J]. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 1992, 29(3): 239-250. | |
| [40] | 周梦岩, 何冬梅, 李亚超, 等. 紫色酸性磷酸酶在植物响应低磷胁迫中的作用研究进展[J]. 分子植物育种, 2021, 19(11): 3763-3770. |
| ZHOU M Y, HE D M, LI Y C, et al. Research progress of the role of purple acid phosphatase in plant response to low phosphorus stress[J]. Molecular Plant Breeding, 2021, 19(11): 3763-3770. | |
| [41] | LI C C, LI C F, ZHANG H Y, et al. The purple acid phosphatase GmPAP21 enhances internal phosphorus utilization and possibly plays a role in symbiosis with rhizobia in soybean[J]. Physiologia Plantarum, 2017, 159(2): 215-227. |
| [42] | 杨海裕, 郑子龙, 刘小林, 等. 基于生态酶化学计量研究小陇山不同植被类型土壤有机碳对微生物磷限制的影响[J]. 西北林学院学报, 2022, 37(2): 1-9. |
| YANG H Y, ZHENG Z L, LIU X L, et al. Effects of soil organic carbon on microbial phosphorus limitation in different vegetation types in xiaolong mountain based on ecoenzymatic stoichiometry[J]. Journal of Northwest Forestry University, 2022, 37(2): 1-9. | |
| [43] | ALLISON S D, VITOUSEK P M. Responses of extracellular enzymes to simple and complex nutrient inputs[J]. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 2005, 37(5): 937-944. |
| [44] | 林惠瑛, 元晓春, 周嘉聪, 等. 海拔梯度变化对武夷山黄山松林土壤磷组分和有效性的影响[J]. 生态学报, 2021, 41(14): 5611-5621. |
| LIN H Y, YUAN X C, ZHOU J C, et al. Effects of different elevational gradients on soil phosphorus fractions and availability in Pinus taiwanensis forest on Wuyi Mountain[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2021, 41(14): 5611-5621. | |
| [45] | YU R P, ZHANG W P, YU Y C, et al. Linking shifts in species composition induced by grazing with root traits for phosphorus acquisition in a typical steppe in Inner Mongolia[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2020, 712: 136495. |
| [46] | LAMBERS H, SHANE M W, CRAMER M D, et al. Root structure and functioning for efficient acquisition of phosphorus: matching morphological and physiological traits[J]. Annals of Botany, 2006, 98(4): 693-713. |
| [47] | 袁颖红, 张文锋, 周际海, 等. 改良剂对旱地红壤活性有机碳及土壤酶活性的影响[J]. 土壤, 2017, 49(5): 909-918. |
| YUAN Y H, ZHANG W F, ZHOU J H, et al. Effects of amendments on labile organic carbon and soil enzymes activities in upland red soil[J]. Soils, 2017, 49(5): 909-918. | |
| [48] | DIPTA B, BHARDWAJ S, KAUSHAL M, et al. Obliteration of phosphorus deficiency in plants by microbial interceded approach[J]. Symbiosis, 2019, 78(2): 163-176. |
| [49] | GILES C D, RICHARDSON A E, CADE-MENUN B J, et al. Phosphorus acquisition by citrate- and phytase-exuding Nicotiana tabacum plant mixtures depends on soil phosphorus availability and root intermingling[J]. Physiologia Plantarum, 2018, 163(3): 356-371. |
| [50] | 张磊, 贾淑娴, 李啸灵, 等. 亚热带米槠天然林凋落物和根系输入变化对土壤磷组分的影响[J]. 生态学报, 2022, 42(2): 656-666. |
| ZHANG L, JIA S X, LI X L, et al. Effects of litter and root inputs changes on soil phosphorus fractions in a subtropical natural forest of Castanopsis carlesii[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2022, 42(2): 656-666. | |
| [51] | YAN Z J, LIU P P, LI Y H, et al. Phosphorus in China's intensive vegetable production systems: overfertilization, soil enrichment, and environmental implications[J]. Journal of Environmental Quality, 2013, 42(4): 982-989. |
| [52] | 王强, 徐建明, 姜丽娜, 等. 平衡施肥对大棚茄子-水稻轮作土壤中作物生产和土壤养分的影响[J]. 浙江大学学报(农业与生命科学版), 2012(2): 197-203. |
| WANG Q, XU J M, JIANG L N, et al. Effects of balanced fertilization on crop production and soil nutrient status under long-term greenhouse eggplant-rice rotation system[J]. Journal of Zhejiang University (Agriculture and Life Sciences), 2012(2): 197-203. |
| [1] | 崔雁娜, 郝贵杰, 王雨辰, 孙博怿, 童喻浩, 朱彦雨, 王敏, 方启航, 施旭梅, 楼逸笛, 朱新丁, 涂金玉, 张海琪, 杨煌朕. 稻虾轮作对稻田土壤理化性状和细菌多样性的影响[J]. 浙江农业科学, 2026, 67(1): 202-210. |
| [2] | 李辉, 林继彤, 邵祺, 娄燕宏, 王会, 杨全刚, 潘红, 诸葛玉平. 不同施肥模式对土壤磷酸酶及其功能基因影响的研究进展[J]. 浙江农业科学, 2025, 66(8): 2032-2038. |
| [3] | 徐有祥, 朱真令, 王昱妃, 江建锋, 杨海峻, 董祥伟, 李诚永, 陈锦鹏, 徐侃, 叶毅豪, 张燕, 王宏航, 邵国胜. 油-稻-豆轮作对土壤理化性质和水稻微量元素含量的影响[J]. 浙江农业科学, 2025, 66(6): 1315-1321. |
| [4] | 郑嫣然, 程艳, 赖齐贤, 蔡为明, 张小明, 金群力, 刘雷, 王寅, 汤勇. 大食物观视角下稻菇轮作技术创意模式发展路径研究[J]. 浙江农业科学, 2025, 66(5): 1291-1296. |
| [5] | 孙晓伟, 姚健, 王京, 何冰, 张幸博, 李建华, 薛刚. 许昌烟区“以烟为主”的轮作套种模式研究[J]. 浙江农业科学, 2025, 66(2): 329-335. |
| [6] | 金梅娟, 李冬梅, 董明辉, 宋英, 王海候, 顾俊荣. 太湖地区稻菌轮作模式下4种羊肚菌品种的适应性及其农艺性状[J]. 浙江农业科学, 2025, 66(12): 3013-3018. |
| [7] | 卜爱爱, 胡娟欣, 方书琴, 薛兆琨, 俞柯汝, 方先芝, 马嘉伟, 柳丹, 叶正钱. 不同改良措施对雷竹林复耕土壤肥力和作物产量的影响[J]. 浙江农业科学, 2025, 66(12): 3066-3072. |
| [8] | 张玉, 李刚, 张秋丽, 宋安易, 张文献. 收获期对瓜-稻水旱轮作模式下稻米品质的影响[J]. 浙江农业科学, 2025, 66(11): 2741-2745. |
| [9] | 方保, 和国优, 沈俊儒, 唐旭兵, 任龙辉, 甄安忠, 兰玉锋, 孔垂思. 不同作物与雪茄烟轮作对根际土壤细菌群落的影响[J]. 浙江农业科学, 2025, 66(11): 2772-2778. |
| [10] | 魏祥帅, 高辉. 淮安市稻麦轮作大面积产量提升面临问题与对策[J]. 浙江农业科学, 2025, 66(10): 2530-2536. |
| [11] | 张志明, 方丽, 郭焕茹, 凡改恩. 水稻轮作和不同土壤处理对甜瓜产量和品质的影响[J]. 浙江农业科学, 2024, 65(5): 1075-1078. |
| [12] | 李诚永, 夏英, 李韵, 李正泉, 徐南昌, 王宏航, 袁敏良. “稻-豆-油”三熟制水旱轮作绿色高效栽培技术[J]. 浙江农业科学, 2024, 65(4): 812-816. |
| [13] | 贾佳, 王斌, 陈新, 叶凯. 东阳元胡-水稻轮作系统价值特点与保护策略[J]. 浙江农业科学, 2023, 64(9): 2128-2131. |
| [14] | 沈月明, 周彬, 何凯波, 张红梅, 沈亚强, 王保君, 杨海龙, 权新华, 程旺大. 水稻-长梗白菜轮作对土壤养分、活性炭、氮库的影响及其效益分析[J]. 浙江农业科学, 2023, 64(9): 2177-2180. |
| [15] | 陆芳, 孙勰, 姜春月, 李月明, 鲁永煌. 化肥减量及菜豆轮作对不结球白菜生产的影响[J]. 浙江农业科学, 2023, 64(7): 1641-1643. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||